

- #MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL INSTALL#
- #MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL UPDATE#
- #MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL PATCH#
See previous section for undoing the changes to your working copy. Notice that this will only undo the committing action. $ hg rollback # roll back the last transaction to deal with typos in the commit log or similar, do: In case you want to undo a local commit, e.g. $ hg revert -a # undo all uncommitted changes to all files. $ hg revert somefile # undo uncommitted changes to this file You can undo all uncommitted changes by doing: This will also use the identity that you specified in your config file. This will open the text editor that you specified in your config file. # if you want to commit only the local directory # even if you are in a sub-directory (this is not as SVN does) $ hg commit # take care, this will commit changes for the whole repository $ hg diff # show differences that are to be committed
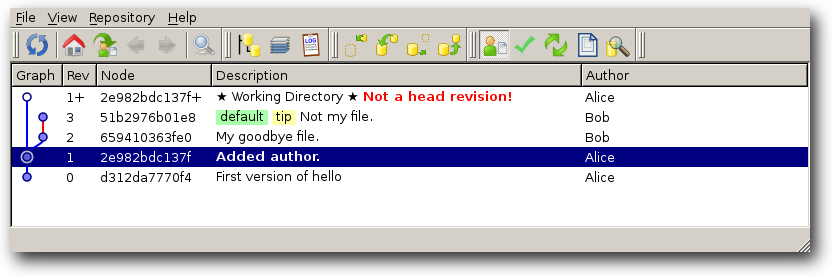
$ hg status # see what files are affected $ hg add # Put a file under revision control $ hg branches # show the list of branchesįirst of all, make sure you have put any new files under revision control: $ hg branch # show the name the current branch Pretxncommit.crlf = python:īy default, what you now see is the development branch, called the 'default branch'. In the end you should be adding something like this to your config file: In order to deal with Windows end-of-line encoding, please follow these instructions. Will be used to credit you, and contact you in case of a problem. Enter your real name and email address.In the above config file sample, note that some lines are placeholders that you must replace with correct values: Put these lines in the Mercurial config file: We recommend using the global config file unless you really know what you are doing. Note that if you need a different mercurial config for another project, you can also use a per-clone config file. On Windows systems, the global config file is Mercurial.ini in your home directory.On Unix-like systems, the global config file is ~/.hgrc.To do so, edit (or create) your mercurial config file. # 'hg pull -u' is the same as 'hg pull & hg update'.īefore using Mercurial to make Eigen changes/patches, please make sure that you have configured it as described in this section. # your working directory to the latest revision. $ hg pull -u # hg pull brings the changes into your store, and -u updates
#MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL UPDATE#
Or if you have a write access to the repository you have two options:Īfter that, to update your checkout (get the new changes made to the repository):
#MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL INSTALL#
If you want a graphical user interface, install Tortoise-Hg, but below in this page we will only be referring to the command-line interface.īelow in this page we explain some usual commands, but Mercurial has lots of documentation available on the Web: If you are using Unix/Linux, just install Mercurial from your package manager.If you are using Windows or Mac, download it from.Installing Mercurial and finding documentation 5 Search and replace on whole directory.
#MERCURIAL WINDOWS TUTORIAL PATCH#
3.4 Splitting a patch into smaller patches.3.3 Pushing many local commits as a single one.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
